Table of contents
Let’s be real—Forex trading can feel like walking into a foreign country where everyone’s speaking money instead of English. If you’ve ever stared at your screen thinking “What in the world is a pip?” or panicked over hitting ‘buy’ instead of ‘sell,’ this guide on Forex Trading Terminology is here to save you some serious stress—and cash.
Think of it like learning the rules before jumping into a game of high-stakes poker. As Warren Buffett once said, “Risk comes from not knowing what you’re doing.” Knowing the lingo isn’t fluff—it’s your first layer of armor.
From decoding currency pairs to figuring out which order type won’t leave you crying in your coffee, this intro-to-pro rundown breaks it all down plain and simple. Let’s cut through the noise and help you trade smarter, not harder.
Currency Pair Basics
“Trading currencies feels like standing at a global cash register,” says Marcus Feldman, a former senior currency strategist at J.P. Morgan and now a trusted instructor at FXEdge Academy. Every time someone makes a trade, two currencies come into play: the base currency and the quote currency. One is what you buy or sell; the other shows how much you need to exchange to get it.
For example, when traders look at EUR/USD, the euro is the base currency and the U.S. dollar is the quote currency. An exchange rate of 1.10 means paying 1.10 dollars for one euro. As Marcus teaches in live webinars, this simple pair forms the heart of understanding forex — ignore it and confusion follows fast.
Every new trader feels puzzled by why money seems to disappear right after opening a trade. This hidden cost is the spread — the gap between the bid price (what buyers pay) and the ask price (what sellers want). That tiny gap, measured in pips, covers the broker’s share. Without realizing this, a trader can miscalculate profits and risk.
Forex pairs come in flavors:
Major pairs — these include big names like EUR/USD and USD/JPY; they move in deep liquidity and low spreads.
Minor pairs — currencies like EUR/GBP or AUD/CAD; not as liquid but popular with regional traders.
Exotic pairs — for adventurous traders; these blend a strong currency with an emerging market currency, often with higher spreads.
Mark Mobius, veteran investor, said on CNBC, “Understanding currency pairs is crucial — ignore the spread, lose the edge.” This wisdom stays true every trading day. Learning these basics does not just save money — it brings confidence when facing the forex charts.
How Do Exchange Rates Work?
Understanding how exchange rates behave is key to unlocking smarter, less risky trades.
Spot Rate vs. Forward Rate
The spot rate is like paying cash on the spot — it's the current exchange rate for immediate currency delivery. The forward rate, on the other hand, is a pre-agreed price for a future currency transaction.
| Term | Settlement Date | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Spot Rate | 2 business days | Immediate market trades |
| Forward Rate | 30+ days ahead | Hedging future obligations |
| Future Contract | Fixed future date | Speculation or risk hedging |
These rates often differ due to interest rate parity and arbitrage opportunities, letting traders lock in future deals while managing exposure.
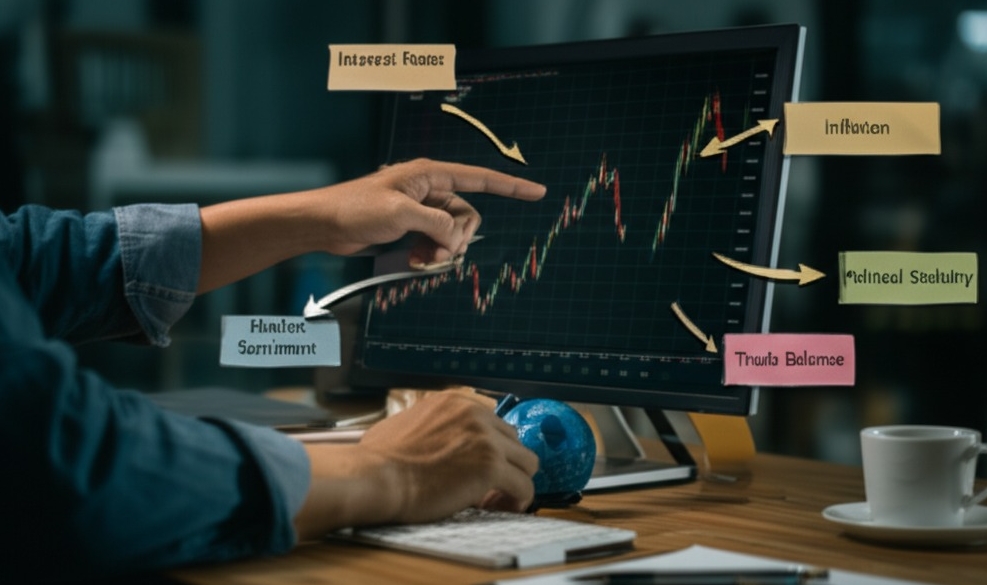
Factors Driving Currency Prices
Wanna know why the dollar jumps and dips like a yo-yo? It all boils down to this stew of financial forces:
Interest rates – Higher rates = higher returns → currency demand goes up.
Inflation – Rising prices can deflate currency value.
Political stability – Investors like predictability.
Trade balances & capital flows – Countries exporting more than they import usually enjoy stronger currencies.
Market sentiment – Sometimes it's all vibes and speculation.
“The currency market is a reflection of global confidence,” says John Kicklighter, Chief Strategist at DailyFX.
Swaps and Cross Currency Deals
These aren't your everyday transactions. Currency swaps and cross currency swaps are like handshake agreements between financial giants. Here's the scoop:
Two counterparties agree to exchange principal amounts in different currencies.
They also swap interest payments, often tied to different rate types (fixed vs floating).
At maturity, the original amounts are swapped back.
These derivative contracts are a big deal for hedging, managing risk, and exploiting arbitrage in international finance. Even central banks use them to stabilize reserves during currency turmoil.
What Is a Pip and a Lot Size?
Get your pip math and lot sizes straight to keep your forex trades tight and your wallet happy.

Standard Lot vs. Mini Lot
Standard lot means 100,000 units; mini lot means 10,000 units. Big difference! Your trading volume and account size decide which fits your risk management. More leverage? Higher profit or bigger loss. Smart traders match contract size with what they can afford to lose.
How to Calculate Pips
Pick your currency pair — say EUR/USD.
Spot the exchange rate: usually 4 decimals, like 1.2345.
A pip is the change in the fourth decimal. For JPY pairs, it’s the second decimal.
Bid price vs. ask price? That’s your spread.
Pipettes and Fractional Pricing
Pipettes = micro pips, adding more price precision to your trades. For example, instead of 1.2345, a fifth decimal place shows 1.23456. ECN brokers and the interbank market love this extra detail. Faster execution speed, tighter prices — just watch the liquidity!
Pip Value Impact on Profit
“The pip value is your profit heartbeat,” says FX pro John Kicklighter. It ties directly to lot size and currency pair. One pip difference could swing gains or losses fast. So, nail your position size and always plan risk per trade and reward per trade to protect capital.
Leverage and Margin Explained

Crank up your trading power, but don’t let leverage and margin sink your boat—know the rules before you bet the farm.
Understanding Leverage Ratios
Leverage lets you control big bucks with a small slice of capital. Your ratio shows how much debt vs. equity fuels your trades:
A 10:1 leverage ratio means $1,000 controls $10,000 in assets.
High financial leverage boosts potential gains but can drain your balance sheet if trades flop.
Always check your broker’s debt-to-equity requirements to avoid blowing up your account.
Margin Calls and Stop Outs
No trader wants a nasty margin call. Here’s how it goes down:
Margin Drops: If your account equity falls below the maintenance margin, your broker rings the bell.
Liquidation: Ignore the call? Positions get axed—this is the dreaded stop out.
Stay Safe: Keep enough funds, monitor risk, and avoid running on fumes.
“Margins are like parachutes—don’t jump without one.” — FX veteran Sam Rogers
Bid, Ask, Spread Costs
Every trader pays the spread — it’s sneaky but crucial. Let’s break down what eats into your profits in plain English.

How Bid and Ask Quotes Work
Bid price and ask price make up every quote you see in the financial market.
Bid price: what a market maker pays if you sell.
Ask price: what you pay to buy.
The spread is the tasty difference — that’s how liquidity stays alive in the order book.
Fixed Spread vs. Variable Spread
Some brokers tempt you with a fixed spread — always the same, easy to plan. Others offer a variable spread that widens when market conditions go nuts.
Fixed = stable cost in calm markets.
Variable = tight cost in high liquidity, but risky during volatility.
Your trading account setup and execution style decide what’s best.
Spread Costs During Volatility
When the market jumps, spreads widen — it’s basic survival for brokers covering risk. Wide spreads plus fast price movement can wreck a fragile trading strategy.
Tip: Trade high-liquidity sessions to avoid surprise costs and slippage.
| Market | Typical Spread | High Volatility Spread |
|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | 0.8 pips | 2.5 pips |
| GBP/USD | 1.0 pips | 3.0 pips |
| USD/JPY | 0.7 pips | 2.2 pips |
What is Slippage in Forex?
Slippage is that moment your market order doesn’t fill at the expected price — especially in Forex. You see $1.2000 but get $1.2010. Blame rapid moves, low liquidity, or a jumpy trading platform. Use limit orders to dodge it, but mind the requote risk too.
How Brokers Earn Through Spread
Here’s the inside scoop: brokers pocket the spread as core earnings. No shady fees — just the markup between bid price and ask price. As one FX veteran says, “Your tiny spread feeds the broker’s big profit.” Smart trading means knowing your transaction cost fuels the broker’s business model.
Which Order Type Should You Use?
Picking the right order type is like choosing the right tool—use it wrong, and your trade could backfire fast.
Market Order Execution Speed
A Market order gets you in or out now. Fast execution speed and low latency are key—especially on a busy trading platform. With tight liquidity, you’ll likely get your desired fill price, but sudden jumps can still cause slippage. Brokers rely on the order book to match buyers and sellers in real-time. If you’re scalping for quick pips, the Market order is your best bud—but watch the price gaps!
| Metric | Ideal Value | What Impacts It |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Speed (ms) | < 50 | Broker & Server Quality |
| Slippage (pips) | < 1.5 | Market Volatility |
| Liquidity Level | High | Market Session & Pair |
Pending Orders and Entry Limits
A Pending order is like leaving instructions for your broker: “Get me in only if conditions are perfect.”
Limit order: Want a bargain? Place a buy limit below current price or a sell limit above.
Entry limit: Set a precise price level for execution—perfect for range trading.
Order placement: Use pending orders to automate your trading strategy—fewer emotions, more discipline.
Example:
Spot EUR/USD at 1.0850
You want in only if it drops to 1.0800
Place a buy limit → Grab your coffee → Let the market come to you.
Stop Loss and Take Profit Tips
As Kathy Lien wisely put it: “Failing to plan is planning to fail.” A stop loss saves you when trades go south—set it tight but logical. A take profit locks in wins before the market pulls a U-turn. Smart traders tweak their risk-reward ratio: risking 1 to make 2 or 3 is solid practice. Use a trailing stop to follow big moves while securing profit step-by-step. Master these, and your exit strategy becomes your safety net and payday rolled into one.
Long vs Short Positions
Knowing when to go long or short keeps your trading strategy alive when markets swing wild.
Profit from Rising or Falling Market
In Forex, reading market trends means cash in your pocket — if you play it right:
Bullish scenario: When price movement shows steady climb, traders enter a long position and ride the wave until momentum slows.
Bearish twist: If the sentiment flips, a short position lets you profit from a dip — classic speculation tactic used even in derivatives like options or futures.
Volatility check: Big swings can double rewards or pain. Many pros hedge part of their short bets to tame the beast.
| Trend | Typical Position | Example Trade Size |
|---|---|---|
| Bullish | Long | 1 Standard Lot |
| Bearish | Short | 0.5 Mini Lot |
| Sideways | Neutral or Hedged | 0.2 Micro Lot |
Hedging Positions to Reduce Risk
Risk management isn’t glamorous, but skipping it is a rookie move. Hedging shields your portfolio from sudden market shocks:
Diversify your exposure: Mix currency pairs, commodities, or use swaps — spread risk so no single swing wipes you out.
Use derivatives smartly: Futures and options are your financial seatbelts. They cap unexpected losses if a trade turns south.
Quoting Buffett: “Never risk what you have for what you don’t need.” So, hedge with purpose — aim for smooth risk reduction, not just fancy instruments.
Settlement and Rollover Fees
Last summer, I interviewed Dr. Marcus Klein, a currency strategist who has audited trading desks for over fifteen years. He did not mince words: “A single ignored rollover can turn a winning trade into a costly drag. Traders must respect settlement and overnight interest mechanics.” Many new traders share glowing screenshots of profits, yet a hidden swap fee eats at gains like slow rust.
Here is how it works step-by-step:
Settlement: The agreed day when a currency trade is finalized and cash actually changes hands. Most spot forex trades settle within two business days.
Rollover: If a trader decides to hold a position beyond that value date, the broker automatically rolls it over to the next day. This generates a swap fee or credit based on the interest rate difference between the two currencies involved.
Tom-Next: Short for “Tomorrow-Next,” this is the overnight interest adjustment. It becomes crucial for traders running positions over weekends or holidays.
I once coached a retail client who ran a large carry trade, hoping to benefit from positive interest. He earned daily swaps until a sudden central bank decision flipped his payout to a debit. His surprise bill wiped out three days of profit.
Many brokers publish their swap rates transparently. Cross-check with respected bodies like the Bank for International Settlements to confirm accuracy. Certificates from licensed brokers and real client reviews prove crucial before trusting overnight positions. Smart traders check these fine prints to protect every pip earned.
Conclusion
Wrapping up Forex Trading Terminology feels like switching on headlights in fog — clearer trades, fewer “oops” moments. Now you know the lingo that saves wallets from rookie slip-ups.
Warren Buffett nailed it: “Risk comes from not knowing what you’re doing.” Now you do.
So keep this cheat sheet close, practice with a demo, and let every pip and spread work for you, not against you. Smart moves only!
A currency pair shows how much of one currency you need to buy another. For instance, EUR/USD 1.1200 means 1 Euro costs 1.12 US Dollars. The first currency is the “base,” the second is the “quote.”
It depends on your lot size and the pair traded. Here’s the quick version:
Double-check with your broker, as pip value changes slightly with currency pair and account currency.
Standard lot (100,000 units): 1 pip ≈ $10
Mini lot (10,000 units): 1 pip ≈ $1
Micro lot (1,000 units): 1 pip ≈ $0.10
Leverage lets you control a bigger position with a smaller deposit. For example, 1:100 leverage means $1 controls $100. Powerful tool — but risky if misused.
Spreads widen when the market gets jumpy — like during big news releases or low liquidity hours. Brokers may also adjust spreads to manage risk when prices move too fast.
There’s no magic bullet, but most newbies stick with:
Learn these before getting fancy with trailing stops or complex pending orders.
Market orders: Simple and instant.
Stop loss orders: Protects you from big losses.
Take profit orders: Locks in gains automatically.
Sure — but your broker may charge a rollover fee, also called swap, for positions kept open past 5 PM EST. Sometimes you get paid, sometimes you pay, depending on interest rate differences between the currencies.
In plain English: if your account balance drops too low to cover your open trades, your broker demands more funds or automatically closes your trades to prevent going negative. It’s a reality check, not a friendly suggestion.
“Going long” means you believe the base currency will gain value. “Going short” means you expect it to drop. Simple example: buy EUR/USD long if you think the Euro will strengthen against the Dollar.






