Table of contents
You’re juggling a few currency trades, feeling good—then out of nowhere, one pair crashes and takes another with it. What just happened? Forex Correlation: Using Currency Correlation in Forex Trading is your guide to understanding how currencies move in sync (or against each other) and why it matters more than you think.
In the words of veteran trader Kathy Lien, “Currency correlation can make or break your risk profile.” Correlation tells you which pairs are best friends and which are sworn enemies—vital info when stacking trades or building a portfolio.
This article breaks down how correlation works, how to measure it, which pairs move together, and how pro traders use it to cut risk and boost strategy. No fluff—just tools, tactics, and the straight-up know-how you can use today.
Currency Correlation Basics
Get a grip on how currency pairs move together—or don’t—and why it can make or break your trading game.
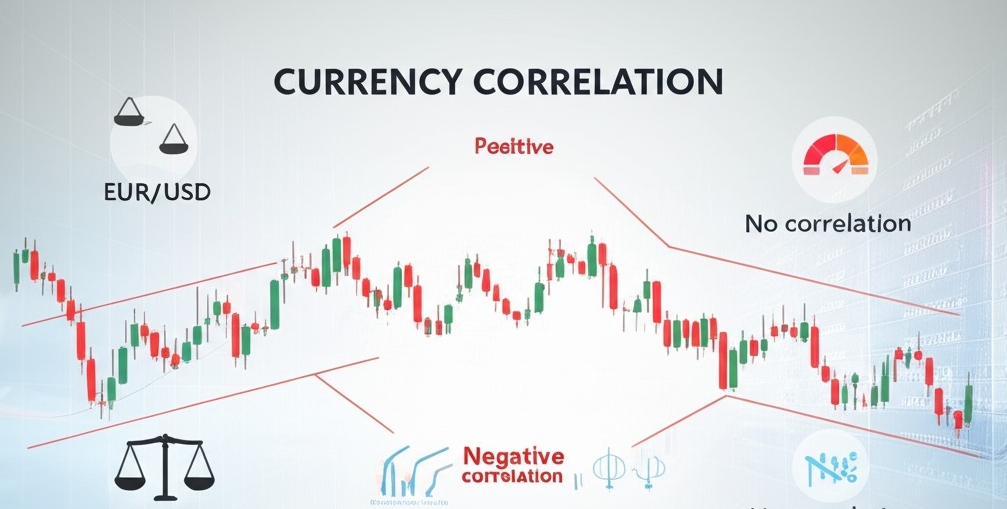
What Is Currency Correlation
Currency correlation is a statistical measure that shows how one currency pair’s exchange rate moves in relation to another. A high correlation coefficient (close to +1 or –1) signals that two pairs tend to rise and fall together—or in opposition.
A positive correlation means they move in the same direction.
A negative correlation means they move in opposite directions.
Zero or near-zero = no meaningful relationship.
In the forex market, knowing this helps with diversification, avoiding overexposure, and better risk management. Traders often use cross-correlation to map out those connections.
Positive vs. Negative Correlations
This part's straight up: are your pairs playing nice or pulling in opposite directions?
Positive correlation: Think EUR/USD and GBP/USD. Both tend to rise or fall together—often driven by USD movement.
Negative correlation: USD/JPY and EUR/USD, for example. When one’s up, the other’s probably down.
The correlation coefficient will tell you how tight that link is.
+1 = strong direct relationship
–1 = strong inverse relationship
“Correlations reveal hidden connections in market movements. Ignore them, and you're trading blind.” – John Kicklighter, DailyFX Chief Strategist
Understanding these relationships helps shape smarter trading strategies, better diversification, and solid risk hedging across asset classes.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Relationships
Currency correlation isn't set in stone—it shifts with time, news, and economic changes.
A long-term relationship shows consistent movement across market cycles.
A short-term relationship might spike from recent economic indicators or volatility events.
Traders often use both fundamental analysis (for long-term) and technical analysis (for short-term signals).
Short-term correlations can break fast—be cautious.
Long-term trends are better for building a broader investment strategy.
Pro tip: Always align your correlation analysis with your trading time horizon and volatility tolerance.
How Is Currency Correlation Measured
Understanding correlation starts with learning how to actually measure it. This cluster covers the practical tools and methods traders use to quantify relationships between currency pairs.

Pearson Correlation in Forex
Pearson correlation is the go-to statistical analysis tool in Forex for measuring the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two currency pairs.
Values range from +1 (perfect correlation) to -1 (inverse correlation).
Traders use the correlation coefficient to anticipate pair movements.
This approach thrives on clean historical data points and consistency.
"Without Pearson correlation, you're flying blind through the markets." – John Carter, author of Mastering the Trade
Timeframe Sensitivity and Lag

You can’t treat a 15-minute chart the same as a daily one—correlation sensitivity changes fast.
Lag creeps in when indicators respond slower than price moves.
Shorter timeframes = more noise, more whipsaw.
Longer periods = smoothed signals but slower to act.
Think of it like watching a movie at 2x speed—sure, you get the gist, but miss the emotional beats.
Interpreting Correlation Coefficients
Here’s how traders read the tea leaves of a correlation coefficient (R-value):
| R-Value Range | Strength | Direction |
|---|---|---|
| +0.80 to +1.00 | Very Strong | Positive |
| +0.50 to +0.79 | Moderate | Positive |
| 0.00 to ±0.49 | Weak to None | Neutral |
| -0.50 to -1.00 | Moderate to Strong | Negative |
Manual vs. Automated Calculations
Manual calculation gets old—fast. Picture typing formulas into Excel vs. letting your bot handle it:
Manual calculation:
Useful for learning, but slow and error-prone
Involves spreadsheet software and static data
Automated calculation:
Uses trading platforms or custom scripts (Python, R)
High efficiency with real-time updates
Great for dynamic trading strategies and backtesting
If you’re still doing it by hand past demo accounts—you’re leaving edge on the table.
Which Currency Pairs Move Together

"One of the most eye-opening moments in my trading career," says Jason Keller, a professional forex analyst with over a decade in the market, "was realizing how strongly some currency pairs mirrored each other. You think you are diversified, then EUR/USD and GBP/USD both tank together."
This kind of positive correlation is common in forex. Pairs like EUR/USD and GBP/USD often move in sync, as both are heavily influenced by the U.S. dollar and Western European economies. On the flip side, USD/CHF and EUR/USD tend to show a negative correlation, meaning when one goes up, the other often slides.
Veteran traders keep a correlation matrix on their desk or trading platform. It shows the correlation coefficient, a number between -1 and +1, indicating how tightly pairs move together. For example:
+0.90 means strong positive correlation (e.g., EUR/USD ↔ GBP/USD)
-0.85 means strong negative correlation (e.g., USD/CHF ↔ EUR/USD)
"Trading AUD/USD without checking what USD/JPY is doing? That is like driving without mirrors," laughs Sarah Lane, lead educator at FXLive Academy. She reminds students to use this data to avoid accidental overexposure.
Experts agree: understanding which currency pairs move together is not just technical fluff—it is the backbone of smarter, risk-aware trading strategies.
Forex Correlation and Risk Control
Trading correlated pairs without understanding exposure? You're doubling down without knowing it. This section shows how forex correlation helps cut risk and control your positions smartly.

Avoiding Double Exposure in Trades
Double exposure is like betting on two horses in the same race—you might think you’re diversifying, but you’re just amplifying your risk. In forex trading, ignoring instrument correlation can lead to portfolio concentration where trades unintentionally move in the same direction, compounding losses.
Smart risk management starts with proper asset allocation.
Use correlation matrices to flag overlapping trades.
Monitor geographic risk and sector exposure, even in forex where macroeconomic themes overlap.
Tip: If you’re long on EUR/USD and GBP/USD, check how tightly they’re moving together—you may have just stacked the same bet twice.
Hedging Using Opposing Pairs
Sometimes the best offense is a good defense. Enter: hedging with opposing pairs. This trading strategy involves going long on one currency pair and short on another that moves in the opposite direction, creating a market neutral position.
Start by identifying negatively correlated pairs.
Use pairs trading setups to hedge directional risk.
Fine-tune your position sizing for beta hedging balance.
“Hedging isn’t about canceling risk—it’s about choosing the right kind,” says John Kicklighter, Chief Strategist at DailyFX. This is key in statistical arbitrage and spread trading strategies.
How Do Traders Use Correlation Strategies
Traders love when things line up—and correlation strategies help make that happen. These methods let you trade smarter, not harder, across currency pairs.
Correlated Pair Trading Systems
Pairs trading is all about finding two currency pairs that move together due to statistical relationships like cointegration. When the spread between them widens or narrows unusually, traders open a long position in one and a short in the other, aiming for convergence.
Market neutral strategy
Requires solid backtesting
"Pairs trading lets you profit from balance, not direction," says FX quant Mike Chan.
Inverse Pair Scalping Strategy
Scalping inverse pairs is like playing ping pong at lightning speed. You're in and out fast—capitalizing on opposite movements in highly volatile pairs.
Spot strong inverse correlation (–0.8 to –1.0).
Wait for a breakout in one pair.
Enter quick counter-trade in the inverse.
This strategy relies on tight spreads, fast execution, and high liquidity. Ideal for adrenaline-driven traders.
Basket Trading With Correlation
Basket trading blends a bunch of currency pairs into one diversified portfolio. It spreads out risk while capturing broader moves.
| Basket Type | No. of Pairs | Avg. Correlation |
|---|---|---|
| USD-based basket | 5 | +0.76 |
| EUR-zone basket | 4 | +0.81 |
| Mixed global set | 6 | +0.58 |
Use a correlation matrix to build the basket, manage risk through smart position sizing, and rebalance regularly to stay sharp.
Diversifying Entries With Correlated Assets
Not every trade should go all-in on a single pair. Smart traders spread entries across correlated assets—like EUR/USD and GBP/USD—so one move doesn't blow the whole game.
Multiple positions = more stability
Timing matters—staggered entries boost flexibility
Great for reducing risk in volatile markets
It’s a solid play for traders who want diversification without straying too far from familiar charts.
Swing Trading Based on Correlation Strength
Swing trading uses medium-term trends, and when combined with strong correlations, it gets even more effective.
Look for pairs moving in sync with +0.8 or higher correlation.
Confirm trend direction with momentum indicators
Align entries on both correlated pairs
Set stops with adjusted risk-reward
It’s about catching waves—not just once, but twice—with strong correlation strength guiding the rhythm.

Real-Time Correlation Tools
“When I first started using a correlation matrix on MetaTrader 5,” says Aaron Vega, a full-time trader and former Barclays FX desk analyst, “it completely changed how I planned my trades.” A growing number of retail and institutional traders now rely on real-time correlation indicators to avoid overlap risk and optimize their trading strategy.
Modern trading platforms like MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 support live correlation coefficient readings using third-party plugins or custom scripts. These tools tap into a live data feed to monitor how one currency pair moves in relation to another across different timeframes.
Correlation matrix plugins for MT4/MT5
Web-based platforms like Myfxbook and Mataf
Heatmaps that track rolling 30-day or intraday shifts
Forex educator Ashraf Laidi recommends real-time tools for “managing cross-exposure on positions that appear unrelated but move in tandem.” These systems highlight strong correlations so traders can avoid doubling down on risk without realizing it.
Award-winning platforms such as cTrader and TradingView offer built-in correlation analysis, backed by regulated brokers and verified data feed certifications. For traders serious about precision, a real-time correlation indicator is no longer optional—it is mission-critical.
Why Do Correlations Break Down
Currency pairs don't always stick together. Here’s why forex correlations sometimes go sideways—often fast.
Impact of Economic News Releases
Economic indicators like GDP, CPI, or the NFP jobs report can blindside correlation patterns. A surprise in retail sales or industrial production, for instance, can spark outsized volatility, breaking expected correlations. When EUR/USD and GBP/USD typically move in tandem, but a strong US jobs report drops one while the other holds steady, that's correlation breakdown in action.
Traders should check economic calendars daily.
Keep tabs on lagging vs. leading indicators.
Remember: market reaction > data accuracy.
“News drives the market—not logic,” said famed trader Paul Tudor Jones.
Central Bank Policy Divergence

When central banks move in different directions—one hikes rates, another holds—correlations wobble. The Federal Reserve could be tightening, while the European Central Bank is still easing. That contrast? It yanks related pairs apart.
Monitor interest rate differentials and yield curves
Watch forward guidance speeches
Compare policy timelines across the Fed, ECB, BOJ, and BOE
Even if two economies are similar, diverging policies can flip the script fast on currency alignment.
Market Sentiment and Risk-On/Off Flows
Sometimes, it’s all vibes. When fear grips the market—like during a war scare or bank crisis—investors flip the switch from risk-on to risk-off. Safe haven flows into the USD, JPY, or CHF break usual pair movements.
| Sentiment Phase | Risk Preference | Likely Correlation Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Risk-On | Buy equities | Higher correlation in risk pairs (e.g., AUD/JPY, EUR/USD) |
| Risk-Off | Buy bonds, safe havens | Divergence in risk-sensitive pairs |
You might expect AUD/USD and NZD/USD to rise together—but in a panic, one tanks faster. That’s sentiment messing with the math.
Advanced Correlation Techniques
Unlock deeper trading insights by blending correlation with advanced tools and strategies.

Multi-Timeframe Correlation Mapping
Want the full picture? Try mapping correlations across multiple timeframes. A currency pair might look tightly linked on the daily chart but act wild on the 5-minute. Mapping helps traders match correlation strength to the volatility and trend of their strategy.
Combine indicator overlays with timeframe analysis.
Watch for correlation flips on higher vs. lower charts.
Always factor in market sentiment shifts when mapping.
Confluence With Technical Indicators
Confluence is your best friend when building high-probability setups. Match correlation trends with RSI, MACD, or even support/resistance zones for cleaner signal confirmation.
Spot a strong correlation move (e.g., AUD/JPY and NZD/JPY trending up).
Add technical analysis layers: a clean moving average crossover or RSI divergence.
Fire only when both the correlation and indicator say “go.”
“Correlation should guide your direction, but confluence tells you when to hit the gas,” says pro trader Rayner Teo.
Using Correlation With Cross Pairs
Trading cross pairs (like EUR/JPY or GBP/NZD)? Don’t ignore the majors that influence them. A move in USD/JPY can ripple into EUR/JPY due to shared currency impact.
Use correlation to manage market dynamics and avoid conflicting signals.
Helps diversify trades while reducing unintended exposure.
Spot arbitrage-like opportunities between major and cross pairs.

Layering Correlation Into Trade Journals
Logging correlation data in your trade journal? Game-changer. You’re not just tracking wins—you’re spotting performance patterns tied to correlated setups.
Note which correlated pairs supported your entry criteria
Add backtesting tags: “Strong correlation with EUR/USD,” etc.
Helps refine exit rules, cut losses faster, and improve consistency
| Trade ID | Correlated Pair | Entry Signal | Result (pips) |
|---|---|---|---|
| #202507 | EUR/USD + GBP/USD | RSI + Support | +45 |
| #202508 | AUD/JPY + NZD/JPY | Trendline Break | –18 |
| #202509 | USD/CHF + USD/CAD | MACD + Resistance | +76 |
Conclusion
You’ve now got the map to see how forex pairs dance together—or trip each other up. Instead of flying blind, you can spot patterns, dodge double exposure, and play smarter.
As trading author Steve Nison once said, “Technical tools don’t predict the future—they help you react better.” That’s what correlation does for your trades.
So next time you load up your chart, ask yourself: Are my positions playing in harmony—or stepping on each other’s toes? Make correlation part of your daily trading rhythm.
Currency correlation is how two currency pairs move in relation to each other. If they move in the same direction, they’re positively correlated. If they move opposite, they’re negatively correlated. Understanding this can help you avoid doubling up on risk or missing out on hidden trading setups.
A lot of it comes down to shared economic drivers. For example, EUR/USD and GBP/USD often move in sync because both are heavily influenced by the U.S. dollar. Sometimes, it's also political events, trade agreements, or even commodity connections (like oil or gold) that link them.
You can use free online tools that update correlations live. Popular platforms include:
Most of them let you adjust the timeframe (daily, weekly, etc.) so you can spot short-term vs. long-term shifts.
Myfxbook Correlation Matrix
Mataf.net Forex Correlation Tool
Babypips Currency Correlation Calculator
TradingView (via custom scripts or indicators)
A hedge using correlation is when you open a position in a second pair to offset the risk of your primary trade. For instance, if you’re long EUR/USD and want to hedge, you might short GBP/USD if they’re closely positively correlated. That way, one can help balance the losses of the other if things go sideways.
Not always. Trading multiple highly correlated pairs at the same time can:
It’s usually smarter to treat them as one trade idea, not separate ones.
Expose you to double risk if the market turns
Inflate your margin requirements
Create a false sense of diversification
Cause confusion when positions move similarly
It’s a number between -1 and +1 that shows how strong the correlation is:
Most tools display this in a correlation matrix, making it easy to scan for opportunities (or risks).
+1 = moves exactly together
0 = no consistent relationship
–1 = moves in exact opposite direction
Markets aren’t static. Central banks shift policy, economies evolve, and global events like wars or trade deals happen. All of that can flip a positive correlation to a negative one overnight. So yeah, what worked last month might not work this week.
Correlation is a great supporting tool, but it shouldn’t be the whole plan. Use it to enhance your:
But don’t ignore price action, fundamentals, or your core strategy in the process.
Risk management
Trade confirmation
Portfolio balancing
Some pairs that typically show high correlation include:
Keep in mind, these relationships shift—so always double-check using a correlation tool.
EUR/USD & GBP/USD (positive)
AUD/USD & NZD/USD (positive)
USD/CHF & EUR/USD (negative)
USD/CAD & Oil prices (strongly linked due to Canada's exports)






