Table of contents
Trading Using Leverage might sound like Wall Street wizardry, but it’s actually a go-to move for everyday forex traders looking to stretch a small stack into a bigger play. Picture this: you’re driving a sports car with turbo—leverage is the boost. When used right, it gets you ahead fast. But take a wrong turn, and things can spin out quickly. That’s the real story behind why traders crave it and fear it.
“Leverage is a double-edged sword,” as Investopedia puts it—sharp on both sides. It's not just about how much you can borrow, but how well you handle the risk that comes with it.
In this article, we’ll break down how leverage works in forex, compare popular ratios like 1:30 vs 1:500, show where to find high-leverage brokers, and share smart ways to stay in the game without blowing your account. Let’s get into it.
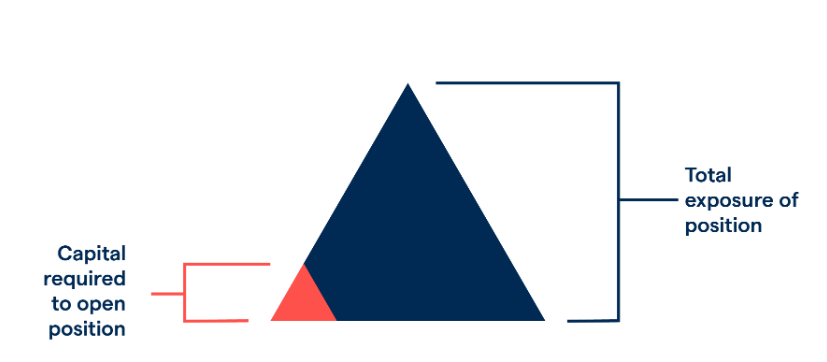
What Is Leverage in Forex Trading?
“Leverage in forex trading is like renting a Ferrari with just enough cash to cover the gas,” said Marcus Wells, a senior forex analyst with over 15 years of hands-on trading experience. “You control a powerful machine with just a fraction of the cost. That kind of access comes with serious speed, but also serious danger.”
In its simplest form, leverage allows a trader to open a position that is significantly larger than the amount of capital they actually have in their trading account. This is made possible by brokers who provide borrowed funds to traders, increasing their buying power in the market.
Essential Concepts You Need to Know
Leverage: The ratio that defines how much larger a position you can control with your available capital. A 1:100 leverage ratio means every $1 of your capital controls $100 in the market.
Margin: The actual amount of capital you must deposit to open a leveraged position. It acts as collateral.
Margin Requirement: This is set by the broker and determines how much margin is needed for a specific position size. For instance, a 1% margin requirement means you must deposit $1,000 to control a $100,000 trade.
Lot Size: This refers to the standardized unit size of a forex trade. A standard lot in forex is 100,000 units of the base currency. Leverage directly affects the lot sizes you can afford to trade.
High leverage can magnify gains/losses in an extreme way. Let us say a trade goes in your favor by 1% on a 1:100 leveraged position—your return is not 1%, it is 100%. But if it goes against you by just 1%, you are down 100% of your capital. That is not theoretical—it happens every day.
According to publicly available records from Finance Magnates, trusted brokers like IG, Pepperstone, and OANDA have won industry awards for transparency and low margin policies. These brokers allow clients to adjust leverage levels manually and educate them on risk.
Experienced traders often take the conservative route. Many stick to 1:10 or lower leverage levels to maintain long-term account health. A recent user review on Forex Peace Army reads:
“I blew my account in two days using 1:500 leverage on a volatile pair. The broker warned me, but I thought I could manage the risk. Lesson learned.”
Traders new to forex often underestimate the emotional toll of high-leverage trades. The stress of seeing your account balance swing wildly in seconds is not for the faint of heart.
Marcus wrapped it up like this:
“Leverage is not evil. It is just misunderstood. It makes good trades better and bad trades worse. Respect it like you would a power tool.”
In forex trading, understanding leverage is not optional. It is the core principle behind how trades are funded, measured, and managed. Every decision—from choosing a broker to managing your risk—ties back to how leverage is used. Ignore it, and you are flying blind.
Leverage Ratio Comparison: 1:30 vs 1:500
Comparing 1:30 and 1:500 leverage isn't just about numbers—it's about your trading goals, strategy, and how much risk you're willing to take.

Pros and Cons of 1:30 Leverage
Leverage at a 1:30 ratio is widely accepted in regulated markets, especially in the EU and Australia. It’s often used by retail traders looking for more controlled exposure.
Advantages:
Lower risk exposure and reduced chance of a margin call
Works well in high-volatility environments
Easier to manage your account balance and losses
Disadvantages:
Slower profit growth, especially on small positions
Requires more capital upfront to make significant gains
Less flexibility for aggressive strategies
1:30 is a good fit for cautious traders or those trading with larger accounts under strict regulatory environments.
When to Use 1:500 Leverage
Using 1:500 leverage gives you much greater exposure to the market with minimal capital, but it also magnifies your risk. This level of high leverage is usually offered by offshore or unregulated brokers.
You're working with a small account and need greater exposure
You trade in stable market conditions with low volatility
You implement tight stop-losses and have strong risk controls
You’re an experienced trader with a high-risk strategy
Important note: High leverage increases the likelihood of a margin call and can liquidate positions rapidly if the trade goes against you.
Leverage Ratios for Day Trading
Day trading with leverage requires speed, strategy, and self-discipline. The leverage you choose depends on your trade frequency and tolerance for fast-moving markets.
| Leverage Ratio | Best For | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| 1:30 | Swing Trades | Low |
| 1:100 | Intraday Trades | Moderate |
| 1:200 | Light Scalping | Medium-High |
| 1:500 | High-Frequency Scalping | Very High |
Scalpers often prefer 1:500 to maximize gains on small price changes, but that comes with razor-thin margins for error. If you're not watching every second, the market might bite.
Choosing Leverage for Forex Accounts
Selecting the right leverage for your Forex account depends on what you're trading, your risk profile, and your broker's options.
Account Type Matters: Micro accounts often support higher leverage, while standard and ECN accounts may have tighter restrictions.
Broker Policies: Regulated brokers in the U.S., U.K., and EU typically cap leverage at 1:30. Offshore brokers may go as high as 1:1000.
Strategy Fit: A long-term investor might stick to 1:30 or even lower. Meanwhile, an active day trader or scalper might prefer 1:200 or more.
Risk Tolerance: Know how much you're willing to lose. If you panic at a 10% drawdown, 1:500 isn’t for you.
“Leverage is a tool. It either helps you build wealth or destroy it. The difference is whether you know how to use it.”
– Anton Kreil, Trading Educator
How Does Leverage Affect Forex Trading Profits?
Leverage can multiply profits fast—but it can also wipe out accounts just as quickly.

Leverage Impact on Winning Trades
Leverage gives traders the ability to control larger positions with a small amount of capital, which can make even small market movements result in big gains—or big losses.
When a trade goes in your favor, leverage can turn a 1% market shift into a 100% return on your invested margin.
But that same leverage can make a tiny mistake costly. If you're wrong, losses stack up fast.
Let’s say you're trading with a 1:100 leverage ratio:
You control a $10,000 position with just $100.
If the price rises by 1%, your profit is $100—a 100% gain on your margin.
But if the price drops 1%, you lose your entire margin.
Leverage doesn't change the market. It changes your exposure. It makes every trade feel like it's in the fast lane, and if you don’t know when to brake, you're toast.
Kathy Lien: “Leverage is a double-edged sword—it can make you rich or bankrupt you in a flash.”
Margin and Profit Relationship Explained
Margin is the deposit required to open a leveraged trade. Your profit is determined by how much the market moves beyond the margin—multiplied by your leverage.
| Leverage Ratio | Margin Required ($) | Profit from 1% Price Move ($) |
|---|---|---|
| 1:10 | 1,000 | 100 |
| 1:50 | 200 | 500 |
| 1:100 | 100 | 1,000 |
| 1:500 | 20 | 5,000 |
Higher leverage = smaller required margin.
But higher leverage also means a smaller cushion before a margin call is triggered.
That 1% price dip that’s harmless with 1:10 leverage? With 1:500, it could wipe out your position instantly.
The takeaway? Use leverage to scale profits strategically, not to gamble. Smart traders use stop-losses and proper position sizing to make the margin-profit relationship work for them—not against them.
High Leverage Forex Brokers
If you're aiming to trade with more power, high leverage is the key—but choosing the right broker is critical.
Best Brokers Offering 1:500 Leverage
Brokers that offer 1:500 leverage give traders the flexibility to open larger positions with a small deposit. It’s especially appealing for those using margin trading on forex or CFD instruments, but not all brokers are created equal.
Here’s a look at a few top-tier online brokers offering 1:500 leverage:
| Broker Name | Account Types | Max Leverage | Minimum Deposit |
|---|---|---|---|
| XTrader FX | ECN, Standard | 1:500 | $100 |
| TurboTrade Pro | Micro, VIP | 1:500 | $50 |
| BlazeMarkets | Raw Spread, Pro | 1:500 | $200 |
| SwiftFX Global | Mini, Standard, ECN | 1:500 | $10 |
Pro tip: Always double-check the country restrictions—some brokers only offer high leverage to non-EU or non-US traders due to local regulations.

Regulated Brokers with High Leverage
High leverage is great, but not at the cost of safety. That’s where regulated brokers come in—they balance high leverage with strong compliance. Look for brokers regulated by bodies like:
FCA (UK)
CySEC (Cyprus)
ASIC (Australia)
NFA or CFTC (US)
These regulatory bodies enforce strict policies on risk disclosures, leverage limits, and investor protection.
“High leverage without solid regulation is like driving a sports car without brakes.” — Jason M., Former FX Compliance Director
Three reputable regulated brokers that still offer high leverage under certain conditions:
FXPrime – ASIC-licensed with leverage up to 1:500 for international clients.
TradeZone Global – Offers 1:500 with FSA registration, commonly used offshore.
OceanMarkets – CySEC regulated; leverage tiered by experience level and client status.
Don’t just look at leverage—check license numbers, client fund segregation, and audit transparency.
Spreads and Fees on Leveraged Trades
A big trap for new traders: chasing high leverage while ignoring trading costs. When using leverage, every pip counts—and so do hidden fees.
Let’s break it down:
Spreads – These vary by broker type (ECN vs Standard). Tighter spreads often come with commission-based accounts.
Commissions – Charged per lot on ECN-style accounts, typically between $3–$7 per round-turn.
Swap/Rollover Fees – These are interest charges applied to overnight leveraged positions.
Slippage & Execution Fees – Common during volatile news events or low-liquidity hours.
Example:
| Broker | Typical Spread (EUR/USD) | Commission Per Lot | Swap Fees |
|---|---|---|---|
| XTrader FX | 0.6 pips | $6 | Moderate |
| BlazeMarkets | 0.2 pips (Raw Account) | $7 | High |
| TurboTrade Pro | 1.2 pips | $0 (Built-in) | Low |
Bottom line: High leverage = higher risk, but unexpected fees can hurt you just as much. Read the fine print. Compare total trading expenses, not just leverage.
Is Forex Trading Without Leverage Safer?
No-leverage forex trading is often seen as a more stable and risk-conscious method.
Trading Without Leverage: Pros and Cons
Forex trading without leverage is like driving with the brakes half-on—it’s controlled and steady, but not thrilling. Still, for many risk-averse traders, it’s the smartest route.
Pros
Reduced risk: With no leverage, you’re only risking what you invest—no surprise losses due to margin calls.
Capital stability: Large price swings won’t wipe out your funds. That makes your capital more stable and predictable.
Stress-free trading: Ideal for traders who don’t enjoy white-knuckle sessions glued to charts.
Cons
Lower returns: No leverage means smaller returns per trade. Gains are limited to actual price movement, not magnified.
High capital requirement: You’ll need more capital to earn reasonable profits, especially in small-pip markets.
Slow account growth: Without leverage, growing your trading account takes significantly more time.
“You trade without leverage, and you sleep better—but you also need patience and deep pockets,” says Mark Raines, a senior analyst at FXFundLab.
Capital Requirements for No-Leverage Trading
If you want to trade forex without leverage, you better come prepared—with real funds. Unlike leveraged trading, where you control large positions with a small deposit, no-leverage trading requires you to fully fund every position.
That means your portfolio, account size, and minimum capital must all scale up.
| Account Type | Minimum Capital ($) | Suggested Portfolio Size ($) |
|---|---|---|
| Micro Account | 1,000–2,000 | 5,000–10,000 |
| Standard Account | 10,000+ | 25,000–50,000+ |
| Professional Trader | 50,000+ | 100,000+ |
To stay afloat without leverage:
Diversify your investments—don’t put all your eggs in one currency pair.
Keep liquidity high, so you’re not stuck in a tight spot.
Always match your trade size to your capital. Overcommitting is a fast way to drain your account.
No-leverage trading may not give you explosive returns, but it provides a slow, methodical path to sustainable growth—and sometimes, that’s exactly what smart money wants.
Beginner Leverage Strategy for Forex
Starting with leverage in forex? Don’t sweat it.
Setting Leverage for First Trades
Getting leverage right from your very first trade can seriously shape your forex journey. Leverage lets you control larger positions with less capital, but it cuts both ways—magnifying profits and losses. So how do you set it up?
Start by considering your account balance and risk appetite. Most beginner traders should stick to low leverage, like 1:10 or 1:30. This reduces risk while giving you exposure to real financial markets without blowing your account on day one. Always set your position size using proper risk management—never risk more than 1–2% of your account per trade.
Your broker will offer a range of leverage options. Here's a table to help you visualize safe starting points:
| Account Balance (USD) | Suggested Leverage | Recommended Position Size |
|---|---|---|
| $100 | 1:10 | 0.01 lot |
| $500 | 1:30 | 0.03–0.05 lot |
| $1,000 | 1:50 | 0.05–0.1 lot |
| $5,000 | 1:100 | 0.1–0.2 lot |
Remember: More leverage = more potential, but also more pressure. Keep your trades tight, and your margin manageable.
Avoiding Common Beginner Leverage Mistakes
Let’s be real—if you're a beginner, leverage can feel like a fast lane. But without guardrails? Total wreck.
Here are some of the most common mistakes beginner traders make when it comes to leverage:
Overleveraging too soon: Going all-in with 1:500 leverage might look sexy, but it’s reckless.
No stop-loss orders: This is like leaving your car in neutral on a hill—eventually, it rolls.
Ignoring trading psychology: Getting hyped by one win or crushed by a loss will mess with your decision-making.
Position sizing errors: Misjudging lot sizes? Classic rookie move.
Avoid these common leverage mistakes by building good habits. Study up on trading education, respect market volatility, and don’t risk more than you can emotionally or financially afford to lose.
“Risk control isn’t optional. It’s the difference between trading and gambling.” – Tina Velasquez, Forex Coach at FXBridge
Starting Small with Micro Accounts
Not ready to throw thousands into a trade? Good—you shouldn’t be. A micro account is your best friend if you're still learning.
Micro accounts (or cent accounts) let you open trades with small capital, often under $50. You're working with real money, but the lot size is tiny, which makes the risk low and the stakes manageable.
Open a demo account first. Get a feel for your trading platform and the order process.
Start with a small initial investment—$10 to $100 is enough to practice with real money behavior.
Choose a broker that supports micro or cent trading. Not all do.
Treat it like the real deal. Use the same discipline you would with a $10,000 account.
Trading with a micro account builds confidence, teaches you platform quirks, and helps develop your strategy—without the pain of big losses. It's not about hitting home runs; it's about learning the game pitch by pitch.
How to Control Risk When Using Leverage
Risk control in leveraged forex trading isn’t optional—it’s survival.
Stop-Loss Strategies with Leverage
A stop-loss order is one of the most essential tools for risk management in leveraged trading. It defines your maximum acceptable loss and automatically closes your position if the market moves against you. In a leveraged trade, losses can snowball fast, so your stop-loss needs to be sharp.
Here’s how to build a reliable stop-loss strategy:
Set your stop-loss beyond normal market noise. For example, place it outside a key support or resistance level.
Avoid placing stops too close when using high leverage—you’ll get kicked out of trades prematurely.
Match your stop-loss size with your position size, ensuring you stay within your loss limit.
Trading without stop-losses is like driving without brakes. Set it, don’t forget it.
Risk Per Trade Guidelines
How much should you risk on a single trade? It’s a crucial question in forex trading. The standard guideline is to risk no more than 1–2% of your total account balance on any given trade. That way, even a series of losses won’t wipe you out.
Use this step-by-step method:
Determine your total capital (e.g., $10,000).
Choose your percentage risk (e.g., 1% = $100).
Define your stop-loss (e.g., 50 pips).
Use this formula:
Position Size = (Risk $) ÷ (Pip Value × Stop-Loss in pips)
By aligning position sizing, stop-loss, and your entry point, you’ll stick to consistent risk management rules and avoid emotional trading.
Using Leverage with Risk-Reward Ratio
The risk-reward ratio is your compass in leveraged trading. It compares how much you could lose vs. how much you could make. A typical benchmark? 1:2 or 1:3. That means risking $100 to make $200 or $300. Used correctly, it lets you profit even with a 40% win rate.
Here’s the deal:
Leverage can inflate both your potential loss and potential profit.
A strong trade setup should have a clearly defined entry point, exit point, and a favorable risk-reward ratio.
Don’t enter a trade unless the numbers make sense. Analysis first, execution second.
Pro tip: Stick to trades that at least offer a 1:2 payoff. Anything less puts too much stress on your win rate to stay profitable.
Capital Preservation Techniques for Forex
Preserving your capital in the Forex market isn't just about winning trades—it’s about not blowing up. When you're using leverage, a small mistake can have outsized consequences. These techniques focus on controlling drawdowns, spreading risk, and building a stable trading approach.
| Technique | Purpose | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Hedging | Offset potential losses | Volatile pairs and news trades |
| Diversification | Avoid overexposure | Multi-pair or asset trading |
| Drawdown Limits | Cap maximum account losses | Automated or manual strategies |
Hedging involves opening a second position that moves inversely to your first, protecting against sudden reversals.
Diversification means not going all-in on one trade or pair. Spread your risk.
Drawdown control limits how much of your account you can lose before you stop trading—this is account protection 101.
By using these techniques, you’re giving yourself more time and space to recover from bad trades and survive long enough to profit.
Conclusion
Trading with leverage is kind of like driving a sports car—it’s fast, exciting, and can get you places quicker, but only if you know how to handle the wheel. Jump in too hard, and you risk spinning out. Pick the right ratio, manage your risk like a pro, and you’ll keep control even when the market swerves.
As Warren Buffett said, “Risk comes from not knowing what you're doing.” So slow down, gear up, and let leverage amplify your skill—not your mistakes.
For most beginners, a leverage ratio of 1:10 or 1:30 is considered safer. It limits potential losses while still allowing for moderate gains. Higher leverage can quickly amplify both profits and losses, making risk management essential.
Leverage in forex trading allows you to control a larger position with a smaller amount of your own capital. For example, with 1:100 leverage, a $100 deposit can control a $10,000 trade. This is done through margin provided by your broker.
However, high leverage also increases risk, so it's best used by experienced traders.
Enables larger trades with less capital
Increases potential for higher returns
Useful for short-term and scalping strategies
Yes, it’s possible to trade without leverage. This means you're trading only with your own capital. It reduces the risk of margin calls and forced liquidations, but also limits potential returns—making it less appealing to traders seeking aggressive gains.
Some offshore brokers offer leverage as high as 1:1000 or even 1:2000. However, traders should be cautious. Regulatory bodies like FCA, ASIC, and CySEC often limit leverage to 1:30 or 1:50 for retail traders to reduce risk.
Yes, leverage increases your profit potential only if the trade moves in your favor. For example, with 1:100 leverage, a 1% move in the market can result in a 100% gain—or loss—on your invested capital.
Margin is the amount of money required to open a leveraged trade
It acts as a security deposit with your broker
Calculated based on trade size and leverage ratio
If the market moves against you, a margin call may occur
Without proper risk management, high leverage can wipe out an account quickly.
Amplified losses from small price movements
Margin calls or account liquidation
Overtrading due to low capital requirements
The right leverage depends on your trading style and risk tolerance.
Start low and adjust as you gain experience.
Day traders may prefer higher leverage like 1:100
Swing traders often use 1:30 or lower
New traders should stick to 1:10 or trade without leverage until confident






